
Do you know what thermal conductivity is?
Thermal conductivity (λ) is a physical property of a material that describes its ability to transfer heat. Corn grain has a relatively low thermal conductivity, making it a good thermal insulator. This property is important to consider during storage, as it limits heat dispersion throughout the grain mass. Thermal conductivity of corn and other products in watts per meter-kelvin (W/(m-K)).
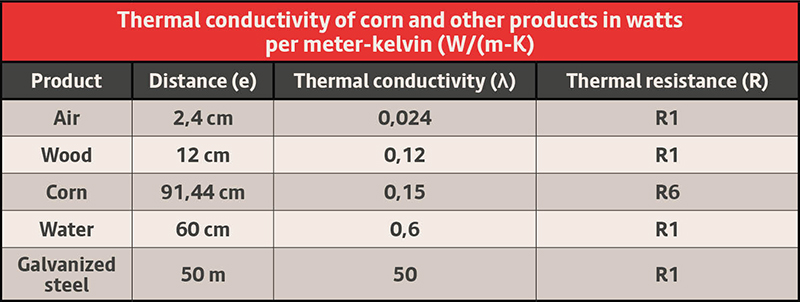
How long does it take to propagate heat through 3 feet of grain?
The time required to propagate heat through a bed of grain corn can be estimated using the thermal diffusion equation (α).
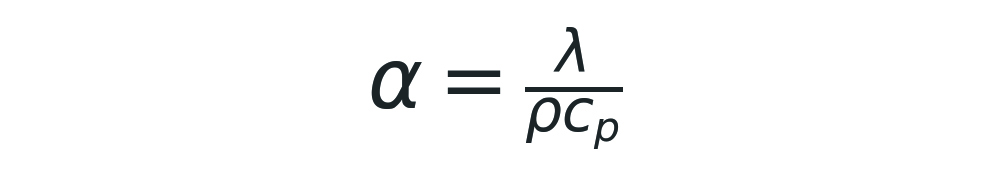 where :
where :
- α = thermal diffusivity (m²/s)
- λ = thermal conductivity = 0.15 W/(m-K)
- ρ = bulk density = 680 kg/m³
- Cp = mass heat capacity = 1350 J/kg-Kr
The characteristic time for heat to propagate over a distance L of 3 feet (0.9144 m) is given by :
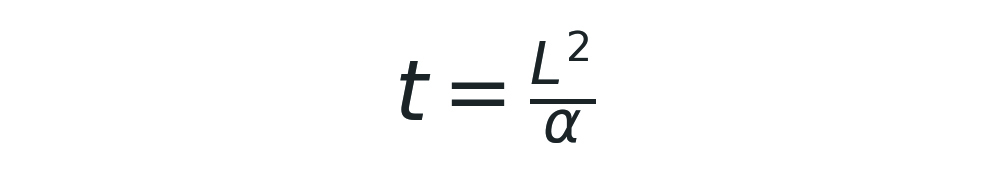 where :
where : - t = thermal diffusion time (s)
- L = depth of corn kernel = 0.9144 m In summary, it would take about 59 days for heat to spread over 3 feet of corn at 14.5% moisture by pure conduction.
To think that a cable system “will tell you when you're going to have a storage problem” is to expose yourself to a significant risk, since grain is insulating and prevents the natural propagation of temperature.
However, regular ventilation can save you a lot of trouble, as it will help remove pockets of moisture that could create a storage problem. After all :
Ventilation = Safety


